Search results
Search for "ferromagnetic nanoparticles" in Full Text gives 11 result(s) in Beilstein Journal of Nanotechnology.
Enhancement of the piezoelectric coefficient in PVDF-TrFe/CoFe2O4 nanocomposites through DC magnetic poling
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2021, 12, 1262–1270, doi:10.3762/bjnano.12.93

- place between PVDF-TrFe and CoFe2O4 nanoparticles, with the formation of a carbonyl group (C=O), as suggested by the FTIR spectra reported in Figure 1. When the DC magnetic field is applied, the ferromagnetic nanoparticles orient themselves along the direction of the applied field and then drag the
Recent progress in magnetic applications for micro- and nanorobots
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2021, 12, 744–755, doi:10.3762/bjnano.12.58

- [50] also proposed a navigation method for two-dimensional robust magnetic resonance of microrobots using ferromagnetic nanoparticles. Laurent Arcese et al. [51] discussed the control design of an intravascular magnetically guided microrobotic system for performing minimally invasive medical
- procedures. The microrobot they designed contained aggregates of ferromagnetic nanoparticles to carry loads driven by gradient magnetic coils. With the help of ferromagnetic nanoparticles, a preliminary study on the navigation method of microrobots in a fluidic environment was carried out, and an innovative
Antimicrobial metal-based nanoparticles: a review on their synthesis, types and antimicrobial action
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2020, 11, 1450–1469, doi:10.3762/bjnano.11.129

- , size and magnetic nature enables them to kill microorganisms through the application of an external magnetic field, resulting in an increase of the therapeutic antimicrobial properties, especially when compared to conventional antimicrobial compounds [136]. Ferromagnetic nanoparticles are probably the
Applications of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles in drug and therapeutic delivery, and biotechnological advancements
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2020, 11, 1092–1109, doi:10.3762/bjnano.11.94

- SPIONs smaller than 10 nm, by Néel and Brownian relaxation for SPIONs between 10 and 13 nm (mechanisms in superparamagnetic nanoparticles), and by hysteresis loss for larger SPIONs (mechanism of ferromagnetic nanoparticles) [139]. Hyperthermia potential and efficacy of SPIONs depend on their structure
Magnetic segregation effect in liquid crystals doped with carbon nanotubes
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 1464–1474, doi:10.3762/bjnano.10.145

- physics of ferronematics and ferrocholesterics (magnetic suspensions of ferromagnetic nanoparticles in LCs) is called the magnetic segregation effect [12]. It has a significant influence on the type of orientation transitions in LC composite materials [40][41][42][43][44], and, as predicted in [39], must
On the relaxation time of interacting superparamagnetic nanoparticles and implications for magnetic fluid hyperthermia
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 1280–1289, doi:10.3762/bjnano.10.127

- not depend explicitly on φ. However, both experimental evidence and Monte Carlo modeling have been provided in [20] to understand the influence of the dipolar interparticle interactions on P*, leading to a reduction of the heating power and consequently on the hyperthermia effects of ferromagnetic
- nanoparticles. For noninteracting MNPs in the dynamic magnetic regime (superparamagnetic regime), it has been shown by Rosensweig in 2002 [21] that only a susceptibility loss mechanism has to be considered (P* ≈ χ’’ where χ’’ is the out of phase component of the magnetic susceptibility). Furthermore, earlier
Magnetic-field sensor with self-reference characteristic based on a magnetic fluid and independent plasmonic dual resonances
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 247–255, doi:10.3762/bjnano.10.23
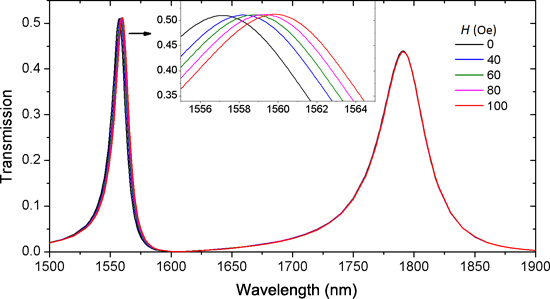
- fluids (MFs) or ferrofluids have attracted a lot of research interest in recent years [1]. A MF is a stable colloidal suspension of ferromagnetic nanoparticles in certain suitable liquid carriers. It has the remarkable property that the refractive index can be tuned in an applied magnetic field [2][3
Dynamic behavior of a nematic liquid crystal mixed with CoFe2O4 ferromagnetic nanoparticles in a magnetic field
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2017, 8, 2467–2473, doi:10.3762/bjnano.8.246

- and only a small distortion angle of the liquid crystal molecular director is observed. A comparison with a previously developed theoretical model confirms this small deviation. Keywords: ferromagnetic nanoparticles; Fréedericksz transition; Introduction Currently, there is a high interest in the
- variations of transition thresholds [27][28] or response time [29]. Ferromagnetic nanoparticles are good candidates for LC improvement due to their significant positive magnetic anisotropy and strong anchoring energy [30][31] on a large surface provided by chain clustering. All these effects help the
- interaction of the liquid crystal with the applied field, the interaction of the ferromagnetic nanoparticles with the magnetic field and the LC molecules anchoring on the surface of the added particles. The deviation angle θ between the glass plates is given by: where z is the Oz coordinate of the LC
Interaction of electromagnetic radiation in the 20–200 GHz frequency range with arrays of carbon nanotubes with ferromagnetic nanoparticles
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2015, 6, 1056–1064, doi:10.3762/bjnano.6.106

- and transmission of electromagnetic radiation. Keywords: carbon nanotubes; electromagnetic radiation; ferromagnetic nanoparticles; magnetic dipole; magnetic nanocomposite; resonance circuit; Introduction Magnetic nanocomposites consisting of ferromagnetic nanoparticles embedded into a matrix
- composed of a porous carbon matrix, ferromagnetic nanoparticles and the interfaces between them [8]. In such systems, accounting for the properties of the carbon matrix, nanoparticles and interfaces becomes of great importance [8]. This issue can be taken into account when considering the CNT-based
- of the NP and of the nanocomposite, which are both positive. Conclusion Problems related to the influence of the conductive carbon matrix, the inductive ferromagnetic NPs and the capacitive interface between the carbon matrix and the embedded ferromagnetic nanoparticles in CNT-based nanocomposites on
En route to controlled catalytic CVD synthesis of densely packed and vertically aligned nitrogen-doped carbon nanotube arrays
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2014, 5, 219–233, doi:10.3762/bjnano.5.24

- be used as high surface area electrodes. Apart from this, the ‘bamboo’-like N-CNTs obtained here could provide a new opening in drug delivery systems due to their rigid ‘needle-like’ morphology. These N-CNTs with a high content of ferromagnetic nanoparticles could potentially serve as magnetically
Enhancement of the critical current density in FeO-coated MgB2 thin films at high magnetic fields
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2011, 2, 809–813, doi:10.3762/bjnano.2.89

- that ferromagnets strongly suppress superconductivity, and even a small ferromagnetic region can be a strong pin, as was confirmed in experiments with NbTi wires containing nanometer-sized arrays of Ni pins [9]. We placed the ferromagnetic nanoparticles on the surface, instead of in the volume of the











































































